The perfusion index (PI) is the ratio between the flow non-pulsatile and pulsatile blood through capillary tissue peripheral.
PI percentage in oximeter normal range:
The normal perfusion index (PI) ranges from 0.02% to 20% showing weak to strong pulse strength. But what does this really mean?
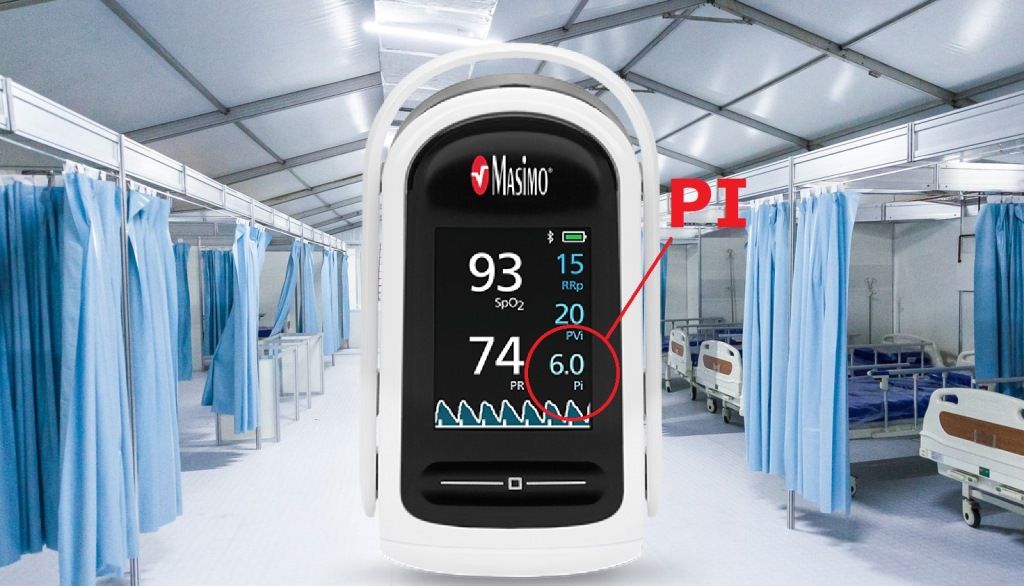
Perfusion Index meaning
Perfusion Index or PI is the ratio of the pulsatile blood flow to the non-pulsatile static blood flow in a patient’s peripheral tissue, such as fingertip, toe, or ear lobe.
Perfusion index is an indication of the pulse strength at the sensor site.
The PI’s values range from 0.02% for a very weak pulse to 20% for an extremely strong pulse.
The perfusion index varies depending on patients, physiological conditions, and monitoring sites.
Because of this variability, each patient should establish his own “normal” perfusion index for a given location and use this for monitoring purposes.
Oximeter pi meaning
The perfusion index is normally monitored with pulse oximeters. PI is also a good indicator of the reliability of the pulse oximeter reading.
For most pulse oximeters for general use, the reading is unreliable or unavailable if PI is at or below 0.4%.
There are oximeters, designed for extremely low PI.
Most people that use an oximeter at home would not need a perfusion index indicator because they are considered to be in generally good health.
A perfusion index adds a lot of sensitivity to the oximeter sensor thus adding to the cost of the oximeter.
Perfusion index normal range
In a hospital, the perfusion index, along with many other parameters, is used to monitor critically ill patients.
Studies have shown that PI has a high correlation with capillary refill time and central-to-toe temperature difference.
In neonatal acute care, a low PI is an objective and accurate measure of acute illness. It is superior to a qualitative approach such as foot warmth.
The perfusion index is also used as an early warning of anesthetic failure. Studies have shown that an increase in PI is an early indicator that general or epidural anesthesia has initiated peripheral blood vessel dilation, which typically occurs before the onset of anesthesia. Lacking the spike would indicate the lack of anesthetic effect.
Other uses of the perfusion index can be found throughout various literature. As we learn more about PI, more clinical applications are being discovered.
Perfusion index normal range chart
Learn from your body by monitoring yourself in the morning, after exercise, or anytime you want to know what your body is telling you. Keep your oximeter at your bedside and each morning monitor yourself before you get out of bed, establish your normal, or “baseline” values.
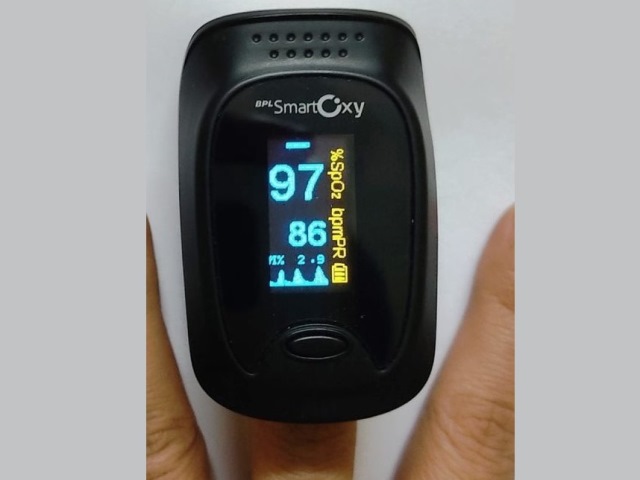
Oxygen saturation (SpO2)
A fully oxygenated body generally means a fully recovered and ready body.
A SpO2 between 97 and 100% means your body is ready!
At higher elevation starting at about 3,000 feet, it is normal for your SpO2 to be 3 to 5% lower. The higher elevation you go, the lower your SpO2 will be.
Pulse Rate (PR)
Your pulse rate changes constantly to provide the necessary blood flow to deliver the oxygen your body needs. Generally, a lower resting pulse rate (40 to 60 beats per minute) means your body is performing more effectively and efficiently.
Perfusion Index (Pi)
Your perfusion rate changes based on whether the blood flow to your body is rising or falling, and whether the arteries in your fingers are narrowing, making your fingers feel colder or widening, causing to your fingers feel warmer.
There is no specific normal value for the perfusion rate, each person must establish their own reference value and observe how it changes over time.
A higher perfusion rate means more blood flow to the finger and a lower perfusion rate means lower blood flow to the finger. Your perfusion rate may or may not change significantly in the morning or after exercise. Write down any changes in your infusion rate and if you feel different when your infusion rate is lower.
PI in pulse oximeter
As the sensitivity of certain pulse oximeters has improved, the fidelity and reliability of PI has improved to a level where clinicians are beginning to explore various ways they can utilize PI to care for their patients
Optimal pulse oximetry monitoring accuracy is dependent on the selection of a monitoring site (fingertip, hand, toe, foot, forehead, ear) characterized by good perfusion with oxygenated blood.
The PI provides instant and continuous feedback as to the perfusion status of the selected monitoring site.
In clinical scenarios where peripheral perfusion may drop below the minimums required for tissue oxygenation and cellular respiration, the PI alerts the clinician to consider another monitoring site.
Optimal monitoring sites are chosen with a relatively high, stable PI.
As an objective indicant of pain levels in patients, the PI has been used to determine proper management of pain, especially in patients unable to communicate their discomfort to the clinician.
The determination of PI is unambiguous and independent compared to subjective means of assessing health status.
Additionally, PI measurement represents a more rapid and inexpensive method to assess peripheral perfusion and circulatory status in comparison to evaluating calf muscle perfusion and oxygen consumption by way of near-infrared spectroscopy.
PI monitoring warrants further exploration for other clinical applications where information on peripheral perfusion or circulatory status would be useful.
Potential future applications include prediction of the success of reimplanted body parts, restoration of peripheral perfusion after cardiopulmonary bypass, and estimation of volume status in trauma patients.
How to monitor my perfusion index?
In a hospital, the infusion rate, along with many other parameters, is used to monitor sick patients. One of the ways to check it at home is with a pulse oximeter:
What is PRBPM in Pulse Oximeter?
The term PRBPM refers to pulse rate (PR) and beats per minute (BPM) and the serious question is what PR and BPM mean on a pulse oximeter.

What are the 2 readings on a pulse oximeter?
A finger pulse oximeter measures two things:
-Blood Oxygen Saturation
-Pulse Rate
Pulse Oximeter Readings Chart
This reading chart provides guidance on what oxygen level means and when and how to seek medical help.
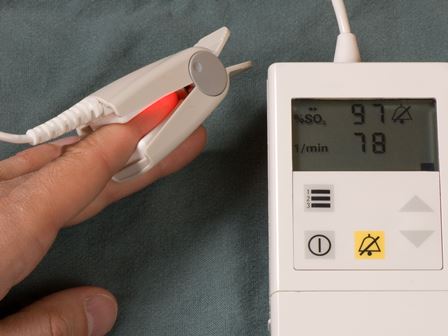
Oxygen saturation machine – Spo2 Machine
A pulse oximeter is an electronic machine that measures the saturation of oxygen (Spo2) carried in red blood cells.
Perfusion Index Normal Range Chart
Understanding the PI Values
