SaO2 is oxygen saturation as measured by blood analysis (e.g. a blood gas) and SpO2 is oxygen saturation as measured by a pulse oximeter. What does this mean?
Measurement of the arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) by pulse oximetry (SpO2), using a fingertip sensor is commonly used in the management of patients with pulmonary diseases.
A SaO2 (arterial oxygen saturation, as determined by an arterial blood gas test) value below 90% indicates hypoxemia, which can also be caused by anemia.
Hypoxemia due to low SaO2 is indicated by cyanosis (a bluish discoloration of the skin resulting from poor circulation or inadequate oxygenation of the blood). Oxygen saturation can be measured in different tissues.
SaO2 vs SpO2
Oxygen saturation (SaO2) refers to the percentage amount of oxygen in the blood. Among other things, it provides information on the functional capacity of the lungs and the efficiency of oxygen transport in the blood.
Oxygen saturation can be determined outside the body using pulse oximetry or invasively with the help of blood gas analysis.
Arterial blood oxygen saturation (SaO2) provides information on the adequacy of respiratory function. SaO2 can be assessed noninvasively by pulse oximetry, which is based on photoplethysmographic pulses at two wavelengths, usually in the red and infrared regions.
Calibration of the measured photoplethysmographic signals is performed empirically for each type of commercial pulse oximeter sensor, using in vitro measurement of SaO2 in arterial blood drawn by co-oximetry.
Due to the discrepancy between SaO2 measurement by pulse oximetry and the invasive technique, the former is denoted as SpO2.
Pulse oximeter manufacturers generally claim an accuracy of 2%, assessed by the standard deviation of the differences between SpO2 and SaO2, measured simultaneously in healthy subjects.
SaO2 normal range
Oxygen saturation (SaO2) levels between 95% and 100% are considered normal. SaO2 levels below 90% (hypoxemia) can lead to health complications, and if it drops below 70%, the outcome can be fatal.
Some of the symptoms of a drop in blood oxygen level below the normal range include rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, chest pain, high blood pressure, dizziness and restlessness, wheezing, and headache.
Oxygen saturation meaning
The following types of oxygen saturation in the blood are distinguished:
- SO2 – oxygen saturation in general
- SaO2 – arterial oxygen saturation
- SpO2 – pulse oximetry measured oxygen saturation
- SvO2 – venous oxygen saturation
- SzvO2 – central venous oxygen saturation
- S⊽O2 – mixed venous oxygen saturation
What is the medical meaning of SaO2?
Is the laboratory abbreviation for Oxygen Saturation,
The main difference between SaO2 and SpO2 is that SaO2, or arterial oxygen saturation, is the percentage of hemoglobin molecules in arterial blood saturated with oxygen, but SpO2, or peripheral oxygen saturation, is the percentage of hemoglobin molecules in peripheral blood saturated with oxygen.
Also, SaO2 can be measured by blood gas analysis, while SpO2 refers to SaO2 measured by pulse oximeter.
Therefore, the SaO2 and SpO2 values may differ as SaO2 measures the oxygen saturation of functional and non-functional hemoglobin, but SpO2 measures the oxygen saturation of functional hemoglobin only.

Spo2 Normal Range by age Chart
If you have breathing problems or have tested positive or are waiting for the test result, a fingertip oxygen meter is a quick and easy way to check the oxygen level in your blood.

Is it Normal for Oxygen Levels to Fluctuate?
Normal oxygen levels can fluctuate based on several factors, such as chronic illnesses, high altitudes, or respiratory illnesses.
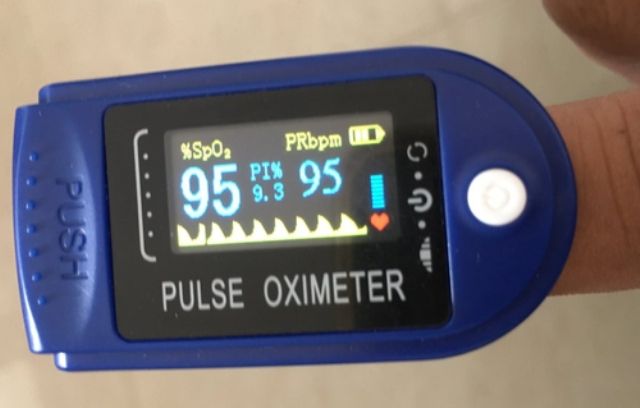
What is Normal Spo2 and pr bpm?
what is Normal Spo2 and pr bpm?
