Forklift Controls Levers: Walk into any warehouse, and one piece of equipment you are sure to see is a forklift. A forklift is a vehicle with a pronged device that is capable of lifting and hauling heavy objects.
Forklifts are capable of maneuvering in small spaces and lifting objects into high-up, hard-to-reach places.
Although forklifts are capable of doing many jobs, they are also dangerous and must be safely operated. Because of their design, forklifts can tip over easily, and they can crush or gouge people or objects if the controls are not handled properly.
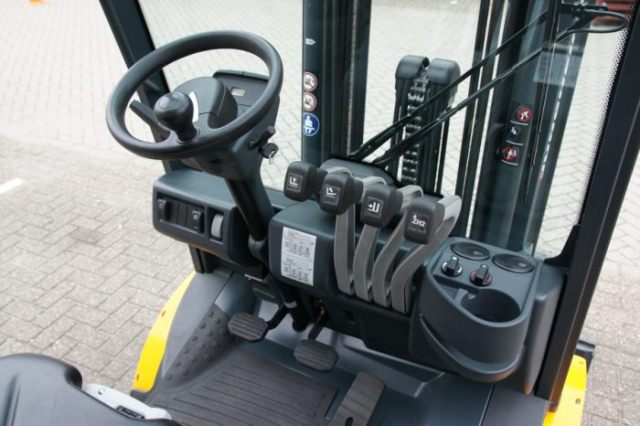

Forklift joystick
Handles forklift controls vary depending on the type of truck. A certain type of forklift can have different operational controls from others.
This is why before operating a forklift, it is important to familiarize yourself with the owner’s manual where you can read the location of the handles controls and understand how each control works.
Hydraulic Lift Knobs: The forklift has three basic control knobs. One that lifts the forks up or down, the second one tilts the forks/blades down or up to secure the load, and the third to move the load side to side.
Some types of forklifts have a knob that controls the width of the fork.
Forklift Directional Controls: This basically works just like the transmission of a car. If you want to park the car, you put it in “P” or park, if you want to drive the car, you put it in “D” or drive, and if you want to reverse, you switch the transmission lever to “R.”
But forklift directional control has only three positions, forward, neutral, and reverse. Forklift directional controls can be steering column-mounted or foot-operated.
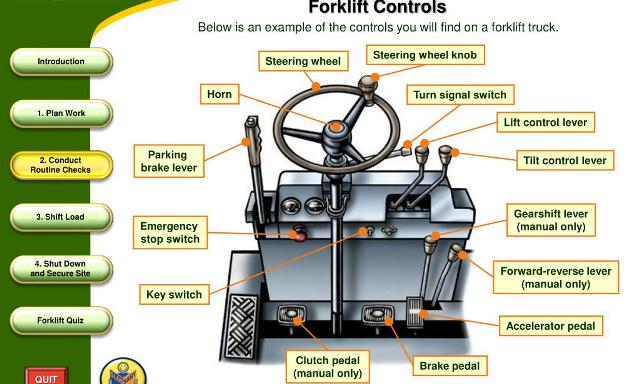
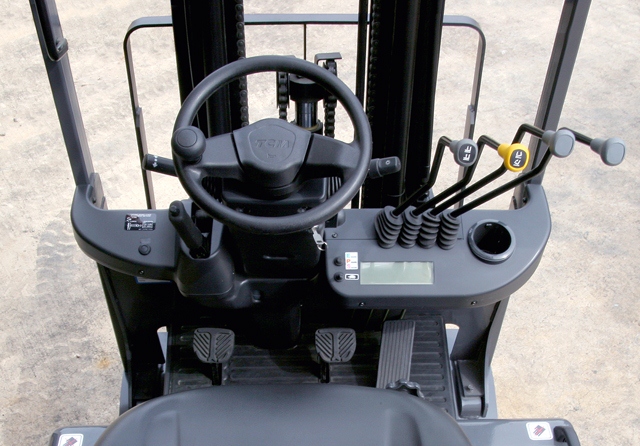
Forklift truck controls
Familiarize yourself with the controls by first reading the owner’s manual. Note the location of each control and its specific function.
Most forklifts have two levers to control the forks. The first lever controls the height of the forks. You pull back on the lever to make the forks go up, and you push forward to make the forks go down.
The second lever controls the tilt of the forks, allowing for better weight distribution, keeping objects from falling off while driving, and helping items slide off when unloading. You tilt the forks forward by pushing the lever forward, and you tilt the forks back by pulling the lever back. Some forklift models have a third lever that controls the width of the forks. Each of the levers is located just to the right of the operator’s seat.
Sit in the forklift and go over the controls with a trained coworker while the forklift is off and not operational. Ask questions if you are unsure of something.
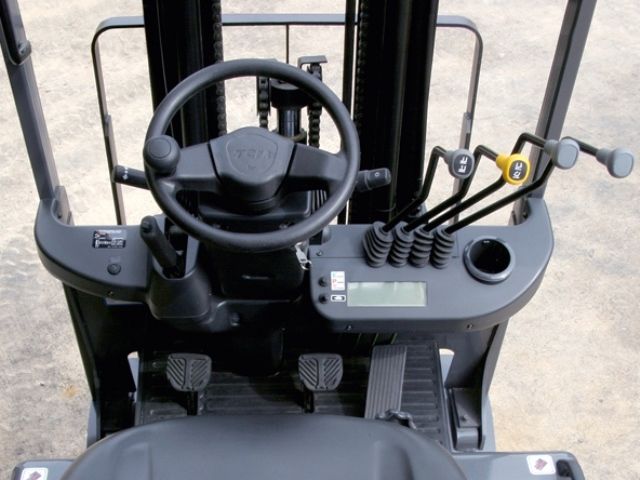
Forklift controls
Observe a coworker as he demonstrates the function of each of the controls. Pay close attention to the individual controls and functions. Watching is often the best way to learn a new skill. Notice that on hydrostatic forklifts to make the machine go, you push on the gas; to make it stop, you release the gas pedal.
There is no brake. Some hydrostatic models have battery-powered engines that shut off when the gas pedal is released and start up again when the gas pedal is pushed again. Hydrostatic forklifts have two gas pedals as well, one for going forward and one for going in reverse. No need to shift into gears; just alternate the gas pedals.
Practice using the controls in an open area without any cargo on the lifts. Before beginning the task of lifting real objects, get a feel for the controls and how they operate by practicing in an area that is free of objects and people.
Understand that the back wheels are what steer the forklift, which can make it feel like you are driving backward and will take some getting used to.

Forklift pedals
Here are the other controls you must familiarize with:
- Accelerator Pedal: This gives a boost in speed and acceleration. It is self-explanatory.
- Brake Pedal: Again, it is self-explanatory.
- Clutch Pedal: Some types of forklifts are equipped with a clutch pedal that gives the operator more driving acceleration by shifting from gear to gear. Such forklifts equipped with clutch are those used outdoors and with an internal combustion engine.
- Inching Pedal: The inching pedal is usually operated by the left foot. Its purpose is to make a very slow and little movement for maneuver with full engine power for lifting. The inching pedal is used commonly to maneuver forklifts in tight spaces or corridors.
- Parking Brake: The forklift is equipped with such a brake and it works similarly to your car. It holds the forklift firmly when not in use. When parking on an inclined floor surface, engage the parking brake and block the wheel to make it more secure.

Hydrostatic forklift
In another type of truck, such as the hydrostatic forklift, acceleration is done by pushing the pedal down and the more the pedal is depressed, the faster the forklift moves; to put the machine to a halt/stop, the operator releases the accelerator pedal. There is no brake control in a hydrostatic truck.
In other types of hydrostatic forklifts, there are two accelerator pedals that act like directional controls. The first pedal when pushed moves the forklift forwards, and the other one moves the truck in reverse. The operator shifts his foot from pedal to pedal to drive the forklift in the desired direction.
Forklift operation safety
Tips on How to Drive a Forklift Safety
Having knowledge of driving a forklift safely can prevent accidents in the workplace. Below are some of the important tips you can employ, you may have heard or known these but still they’re not obsolete.
forklift cert
First and foremost, the operator must be trained and certified first before operating this machine – The forklift training course should be specific to the type of forklift the operator is intending to operate. Taking the course and getting certified only takes a small amount of time to complete and a little investment to spend. Being certified has a lot of advantages.
PPE requirements for forklift operator
Appropriate clothing must be worn – PPEs such as a hard hat, luminous safety vest, steel-toed shoes, and eye protection are important especially when the environment is hazardous. Any loose clothing is not allowed as it can snag with the moving mechanism of the forklift.
Forklift daily inspection
Pre-operational inspection must be performed: a daily inspection checklist must be updated to make sure that the forklift is in good running condition.
The inspection involves checking brakes and hydraulic fluids, seeing if the warning devices and lights are functioning, and ensuring the tires are not worn out. The inspection checklist has the details of all things to check. Any fault should be reported to the superior for immediate corrective action.
Forklift battery charger
The forklift should be fully charged (if it’s electric) or has enough fuel (if it’s gas or LPG-powered) – If the truck has not had enough charge or fuel during operation, it could stop at any time or the truck’s lifting capacity could considerably decrease. What if the operator is lifting a 1-ton load when the truck suddenly stops because of insufficient fuel? This is when a serious accident could happen.
Forklift weight capacity
Never lift a load that is beyond the lifting capacity – know the capacity of the forklift on the data plate, it is usually attached to the machine. It indicates all relevant information such as the model, year, manufacturer, capacity, fuel type, etc. Please do remember that lifting a load that is well beyond the capacity could cause a tip-over.
Overloading is one of the common unsafe practices forklift operators do we’ve observed over the years in this business.
Forklift lifting capacity
When lifting, make sure the loads are evenly balanced and distributed – proper weight distribution is the key to making the load secure during transport. When loading the goods, the heaviest ones should be as close to the truck’s mast.
One important piece of advice when loading large rectangular boxes is that the boxes should be arranged widthwise and not the other way around, the idea is to prevent the load center from shifting forward which could cause the forklift to tip over.
Forklift refueling procedures
Refueling or recharging must be performed in a well-ventilated location – Many of us may perceive refueling/recharging as a simple task to do but make no mistake.
It is one of the hazardous things you do with a forklift. To avoid an accident during this activity, make sure the forklift is NOT running as it has the probability to cause ignition, and that any naked lights and smoking are strictly prohibited in the refueling location.
When recharging an electric forklift, please do remember that recharging should be done only when the charge capacity reaches below 30%.
Avoid over and undercharging the forklift battery as it shortens its lifespan. The charging facility must be equipped with first-aid devices and a wash station in case the battery acid comes in contact with the eyes or skin.
Forklift parking area
Park the forklift in a designated area – when the work shift ends, park the forklift in a designated location, the company usually assigned a place for this. When shutting down the truck, lower the forks touching the ground so that the parking brake is pressed before leaving. Do not leave the key in the ignition.
Don’t park the equipment near the emergency door or exit or in the fire lane as it can block the moving vehicle in and out of the premise.
Forklift safety ebook
- Did you know that there is a guide on how to drive a forklift?
- How to improve forklift safety?
- Forklift safety tips workplace
- Forklift safety tips for pedestrians
“The Guide to Forklift Training” is an essential resource for anyone who operates or manages a forklift. This book covers everything from the basics of forklift operation to advanced safety techniques, providing readers with the knowledge and skills they need to operate forklifts safely and efficiently.
With practical tips and real-world examples, this book is an invaluable resource for anyone who works with forklifts.

Forklift driver training
OSHA Compliant Forklift Operator
COMPLETE Training Kit
- Certificates Of Completion,
- Operator Cards,
- Student Hand Outs,
- Hands-On Evaluation Checklist, & More!
- The new release’s limited-time special promotion pricing ends soon!
- Buy once & get free templates for life to train all your employees!
- English and Spanish versions are both included!
- Get your employees forklift certified in 1 hour!
- Available on a flash drive for ease of use and re-use.
- We have helped thousands stay OSHA compliant
- The best part is that you can complete the training from anywhere at any time!
- It comes with a 100% 30-day money-back guarantee so you can try it out completely risk-free!
How to operate a forklift controls?
Forklift controls vary depending on the type of truck. A certain type of forklift can have different operational controls from others.
This is why before operating a forklift, it is important to familiarize yourself with the owner’s manual where you can read the location of the controls and understand how each control works.
Plugging, also called regenerative braking, regen, or switch-back occurs when an operator traveling in one direction uses the directional selector to switch to the opposite direction.
While it is not illegal to drive a forklift truck on a public highway, depending on the distance it is likely to travel, there are specific legal requirements. For a vehicle to be used on the public road, it must comply with insurance, licensing (tax) and registration requirements.
Lower the forks to the floor when parking the forklift. Make sure that the forks touch the ground when you are leaving. Apply the parking brake when it is idle position. All operational controls of the truck must be in the neutral position before the driver alight the forklift compartment.
The load center is the distance from the face of the forks to the load’s center of gravity. Many forklifts are rated using a 24-inch load center, which means that the load’s center of gravity must be 24 inches or less from the face of the forks.
The most read

Forklift Pedals Explained
How many pedals do a forklift have? What are the 3 pedals on a forklift for?

What are the 4 Levers on a Forklift?
What do the levers on a forklift do?

How to drive a Forklift?
How to drive a forklift for beginners? How to become a forklift driver?

Forklift Safety Procedures
Forklifts are extremely useful workplace vehicles, learn about the rules for driving forklifts.
