Forklift Fork dimensions: Forklift forks, also known as tines or blades, are used to lift and carry loads. They are an integral part of the forklift and ensuring you are using the correct ones and that they are in good condition is essential to both the safety of personnel, but also the forklift and the load.

Forklift fork dimensions and specifications
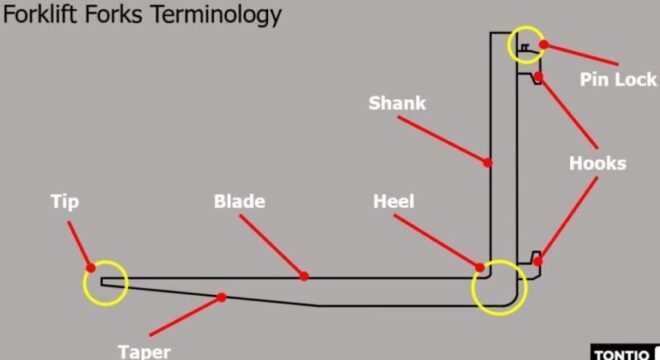
- Forklift blades: Horizontal part of the fork which lifts and supports the load
- Tip: The end of the blade that is inserted into the load
- Shank: The vertical part of the fork
- Heel: Part of the fork where the shank and blade meet
- Hook: The hooks are the elements on the shank that support the forks on the forklift.
- Pin lock (or locking pin, latch pin). Positioned on the top hook and used to position the forks on the forklift carriage. The forklift fork pin can be a latch or button (mushroom) type.
- Taper: The difference in thickness between the tip and the heel. Tapers can begin at the heel or anywhere along the blade.
Production standards for all forks are based on common key- features:
Innovative and highly automated production process.
- Prime quality steel offers good welding characteristics and strong resistance to wear.
- Automated welding of upper and lower hooks with a robotic system, granting better quality of welding, quality repeatability, and higher process speed.
- Complete heat treatment with hardening and tempering on the entire fork, providing the best quality and reliability characteristics.
Standard Forklift Fork measurements
-Standard forklift fork sizes
-Standard forklift fork length
-Standard Forklift Fork dimensions:
- General: Fork-correct dimensioning and conditions are essential for safe, cost-effective, and damage-free pallet handling operations. Therefore, a regular fork inspection system should be put in place to ensure perfect operating conditions. Inspections, repairs, or replacements shall be carried out as a pair.
- Height difference in fork tips: Check a pair of forks mounted on the fork carrier to detect a difference in tip heights. If the difference in tip heights exceeds 3% of the blade length, the pair of forks shall be withdrawn from service.
- Wear: Forks must be checked regularly to ensure the heel thickness is not less than 10% of the original thickness as per ISO 5057. If the fork thickness is less than 10%, the fork must be replaced or related.
Forklift fork inspection
Forks in use shall be inspected at intervals of 12 months or less depending on the possible severe application, multi-shift operation, and fork conditions.
Regular inspections should be carried out by trained personnel. In case of detected damage, failures, deformations, etc. forks shall be withdrawn from service and not be returned to service unless satisfactorily repaired or related.
- Cracks: Check visually the inner heel and top and bottom hook areas to detect possible cracks. Apply non-destructive crack detection tests if necessary. If surface cracks are detected, forks should be withdrawn from service.
- Straightness: Check the straightness of the upper face of the blade and the front face of the shank. If the deviation exceeds 0,5% of blade length or shank height, the fork shall be withdrawn from service.
- Angle: Check the fork’s upper face of the blade to load the face of the shank. If the fork has a deviation greater than 3 degrees from the original specifications, the fork shall be withdrawn from service
- Locking devices: Check the fork positioning locking to ensure their normal operation and wear conditions. If any fault is found, the fork shall be withdrawn from service.
- Marking: Forks shall be marked with the nominal capacity and load center according to ISO 2330. If the marking is not clearly legible, the fork shall be withdrawn from service.
- Hooks: Check the fork hooks for possible wear, damage, and cracks. If the clearance between the fork and fork carrier is visually excessive, forks shall be withdrawn from service.
Replacement forklift forks
Repairs and tests: Repairs should be decided or carried out by authorized, expert personnel only, in accordance with the recommendations of the fork manufacturers. Do not repair surface cracks or wear them by welding. In case of repairs requiring fork re-setting, forks should be subjected to an appropriate heat treatment.
Forks subjected to repairs different from repairs or replacements of the positioning lock and/or marking can only return to service after having passed a yield test as described in ISO 2330.

Forklift pre-shift inspection
The best way to inspect forks is to use a fork caliper.
- Determine the nominal thickness of “N” of the fork. Measurement has to be done on the fork shank using the caliper ruler.
- Position the caliper at the end of the heel internal radius with the opening corresponding to the nominal dimension “N” (eg. for N 45 use 45 mm thickness), where the wear is higher.
- If the fork enters the opening, it is mandatory to replace it. DANGER OF BREAKING. Furthermore, a 10% reduction in fork blade thickness results in a 20% reduction in operating capacity
Types of forklift forks
Following is a list of some of the special types of forklift forks, used for specific applications.
- Pin Type & Bar Type: the forks have a guide and are attached to a shaft. Found on larger lift trucks and construction machines such as some telehandlers. Pin-Types can come with a lower hook
- Drum handling forks: these forks have a section cut out of the side of the forks to enable a drum to be lifted
- Coil handling forks: the inside edge of the forks is “chamfered” to provide a surface for the coil to sit on.
- Explosion-proof: if the forklift is to be used in explosive environments then the forks are clad in stainless steel to prevent sparking. The stainless steel coating is typically 2mm thick
- Forks for the food production industry: forklifts that are used in the food industry are typically clad in stainless steel as they are regularly washed down to maintain cleanliness.
- Lumber forks: have a thin and wide blade for ease when inserting into loads
Lifting equipment
The lifting equipment on forklift truck machines is characterized by robust and high-quality design and numerous options combined with excellent visibility. Forklift trucks can offer many different types of masts all of the clear view designs. In combination with forks and/or attachments, it can provide the handling solution to meet your needs.
For even better handling, there are also a number of intelligent functions for forklift machines:
- Pre-selected lifting height – the operator can simply find the right lifting height by means of 15 pre-selected lifting heights.
- No chain slack – the chains are kept tensioned at all times, eliminating undesired movements of the forks or the attachment.
- Vertical hold– the automatic tilt device ensures that the load is taken up and put down vertically to the loading surface.
Forklift Masts Types:
- Single-stage mast forklift
- 2-stage mast forklift
- 3 Stage Mast Forklift
- Quad mast forklift
What type of steel is used for forklift forks?
They are made of different types of steel. Sometimes HSLA A572-50 (high strength low alloyed) steel, 1045-1060 heat-treated material, T1 heat-treated steel, and others.
The forks on a forklift are used to make direct contact with a load for transport. They are attached to the forklift carriage and are designed to carry a load from the bottom. Forklift forks come in all shapes and sizes. There is a wide variety of fork types available for various applications.
4-Stage – A quad or four-stage mast is designed for very high stacking. Quad masts allow for a shorter collapsed height when compared to a three-stage with equivalent MFH (maximum fork height).
What size forklift should I get for my warehouse?
It is often a question asked by business owners and operation managers. Forklift Dimensions can be tricky and unique to every application. Virtually every forklift dimension could potentially impact an operation, and create a safety hazard if not specified correctly and carefully.
The most read

Forklift Fork Size Chart
Forks are often overlooked on a forklift due to their simple way of operating.

Forklift Classification Chart
Since there is a wide selection of models, it can be difficult to select a forklift.

How wide are forklift forks?
Knowing the different sizes of forklifts
What should I know for my warehouse or workshop?

Forklift Fork Thickness
Inspection of the forklift fork thickness and condition of the forklift should absolutely be part of every daily checklist.
