Tower Crane Specifications: The study of the tower crane will include knowing the structures that make it up, as well as knowing the elements that are part of this and that will allow the crane to perform the tasks for which it has been designed. A description will be made of the main elements that allow the operation and safety of the crane, and the first steps will be taken to design and select several of these elements, understanding that for a deeper design it would require much more complex studies.

Industrial hooks
The lifting hooks must be of reflective striking color and must have a lock that prevents the accidental release of the load, have the embossed printing capacity and must not undergo permanent deformation when they are tested with a load of two. times higher than the nominal load capacity.

Crane wire rope
Steel cables are normally used for lifting (lifting), pulling, lashing or fixing various elements and is the most important element of a Tower Crane, after the control and operation mechanisms, this element joins the load to the crane and actively participates in all the operations of the equipment.
Technical specifications of the cable: The choice of the characteristics of each cable, is made according to the efforts to which they are subjected, which corresponds to precise rules that must be observed and respected.
The steel cables consist of a set of strands and a central core. By combining the wires and strands properly, cable types are obtained from different constructions and for different uses.
Each steel cable must be adapted to the functions it fulfills in each equipment.
Normally, the constructors of the equipment recommend a certain type of cable, this must be strictly complied with.
Steel wire
When replacing a cable, one must be used that has identical characteristics to the initial cable, same diameter, same construction, equivalent resistance and identical type of wire with its similar protective coating.
If an inadequate cable is used, it can mean a sudden break or accelerated wear, with spectacular destruction.
These instructions are complemented with tips for uses for operators and mechanics and with a manual for the revision and control of cables for mechanics, assemblers, and mechanics of maintenance.
The cables of elevation and those of traction do not have to present splices or unions and work with a coefficient of utilization minimum of 6.
Ku = Cre / Q> 6
- Cre: Is the effective breaking load of a new cable
- Q: It is the static traction exerted on the cable
- Ku: Coefficient of cable utilization
In the case of horizontal booms, the minimum effective breaking load of the traction cable, when new, must be at least equal to four and a half times the maximum effort applied to the cable by the traction mechanism, during the start and braking.

Cable connectors
There are several techniques to join a cable:
- By means of a temporary union, where 2 cables of the same diameter are placed in parallel, and a number of clamps determined by the norm are placed.
- Eye to eye joint, where eyes are used in each cable and these are joined by hooks or hooks are attached directly.
- By means of braid, basically, it consists of removing some strands of the cable and replacing them with the strands of the other cable and weaving the whole system.
- The element that secures or fixes 2 cables is called saw – cable or clamp, there are different types, in our country the most used is the Crosby.
Crane cable
Uses of steel cables:
- Elevation, which is an anti-rotation cable, very sensitive to the cavities and hernias, and subject to great traction efforts.
- Carriage, which is a normal construction cable, subjected to drag and friction loads on smaller diameter pulleys; therefore subject to wear by rubbing.
- Brake cable and other emergency types, it is a cable without special mechanical qualities, it is only a rigid cable of command.
- Strobe cables, which are cables subjected to friction and deformation, but which are usually resistant to mistreatment, when they are built with suitable cables, when using anti-rotation cable it is necessary to take care of the inspection and retighten the shackles.

When to change a steel cable
Inspection intervals: The standard on inspection instructions of a steel cable according to international standards establish maximum inspection periods, whose maximum interval must be strictly complied with.
- 12 months for any cable.
- 3 months for cables that raise personnel.
- 2 months for Tower crane cables.
- The cable of a crane must be severely inspected, before and after assembly.
In the latter case, it is necessary to review possible cracks or permanent deformations and should have a record of the person who made the review and the professional who controlled the inspection, this is the only way we could present ourselves before the authority, in the case of a serious accident.
Cable anti-rotation
When the outer and inner layers of the cable are in opposite directions, the tendency to rotate is counteracted with each other.
When the ends are not properly sized, the core can slip or come off at the other end of the cable or through an outer layer
Wire rope lubricant spray
Grease for steel cables:
Normally, the cables must remain greased because their construction needs it to avoid internal friction.
Normally, the manufacturer’s instructions must be respected, with regard to the lubricant to be used and the environment where the equipment is working.
They should always request instructions from the Chief Maintenance Engineer.
There are some cables that are never greased, such as those of tirfor, of strobes or another system that swallows cable.
Crane inspection
Visual control:
- The cables must be inspected periodically to check their evolution and wear.
- If a cable between one control and another, shows a major change, appear steel blades, cut wire, thins in one area, or one notices the soul or the pack of loose inner screws, the cable must be replaced.
- The cable must be washed and then carefully revised, an easy way is to put on a glove and tighten the cable with a quantity of fine cloth, and start a route of the cable, in all the areas that the cable is entangled with the cloth, it is necessary to Note the reason, they are usually cut strands or deformations.
- Then you have to re-lubricate the cable.
Critical areas:
Always in a crane cable, there are areas that present greater wear, than others, in this part of the cable it is necessary to maintain a special vigilance, especially when the cable starts to get “hairy”.
Abnormal Deformations:
In some cases, the cable starts to show a lot of brightness, irregular flattening, or unexpected thinning. In this case, you should always check:
- Catalinas, which may be locked, derailing the cable or throat with damage.
- Great crushing, the winding drum may be defective.
- With a very rare waist, the cable has been stretched abnormally and it is likely that the central package or the soul has been released.
- Very dry cable; check the inner friction because there may be played between the strands. Naturally, that is a lack of lubrication or poor quality of this.
Tower crane spare parts
Causes that force a replacement:
- Rupture of more than one strand.
- If there is a knot
- Existence of a hernia.
- Abnormal diameter reduction
- throat formation
- thinning of a section.
- When the cable anywhere has decreased by 10% of its diameter
- When there is more than 20% hairy surface (with wire strands) in an area less than one cable passage.
- If a strand decreases 40% of the diameter and is released in two cable passages
- When internally presents a high degree of oxidation.
- When a cable has been strangled, by placing a Crosby shackle in a defective manner.
Pulleys and gears
The winding drums and the grooves of the different pulleys must have smooth surfaces, they must be provided with side discs or other elements that prevent the cable from coming out.
Technical specifications
The radius of the disk must exceed the last layer of cable in at least 2 times the diameter of the cable. Whatever the working position of the drum, they must remain at least three turns of wire.
The diameter of the drums (D), measured at the bottom of the throat, must be equal to or greater than 20 times the nominal diameter of the cable (d). If the drum is smooth D increases to 24.
The diameter of the pulleys, measured at the throat bottom, must be equal to or greater than 22 times the nominal diameter of the cable.
The effective diameter of the cable that is used on a slotted drum or a pulley with a throat must not be greater than the width of the grooves of the drum or the throat of the pulleys.
The struts that make up the lifting gear must be equipped with protection devices, which avoid inserting the hands between the cable and the throat of the pulleys.
Tensioners for steel cable
Fixing technique: The cable fixing system must comply with the provisions of the standards
The carrier cables of the distributor carriage must be anchored in the opposite direction on the winding drum.
The operation exclusively friction is not accepted (except for cranes in which the force used to move the car does not exceed 10 kN and cranes manufactured before 1990).
Drum for steel cable
Transfer of cable to drum: Manufacturers recommend transferring from above in the upper direction for the anti-rotation cables.
It is important to comply with this instruction by breaking the rope carrying drum so that the winding on the drum of the machine remains with relative tension.
The cable must not be dragged along the ground, because the lubricant picks up abrasive particles, which deteriorate the wire.
When transferring a cable from one reel to another or to the drum of a machine or equipment, the cable must pass from the top of one another, or from bottom to bottom.
Steel flange
When a load is lifted, it is usually necessary to use an auxiliary element, making a connection between the load and the hook of the crane. This element is called a flange.
Generally, this operation keeps a load suspended, which we can call a restricted airway. It is very important in this operation to take the necessary precautions, so as not to suffer an undesired accident, due to material fall.
There are different types of flanges, in most cases, prefabricated solutions are used, which can be constituted by one or more flanges which are usually constructed of:
- Steel cables: strobes
- Flat ribbons made of synthetic fibers: slings
- Steel links: chains
- Woven vegetable fibers: rope rigging
- Woven synthetic fibers: rope rigging
These solutions are prefabricated and must comply with common safety standards valid for all, plus each must be complemented with the particular rules for each flange.
When using mixed flanges both must be complemented rigorously in each particular case.
Tower crane safety
- You must always know exactly the weight of the material to hoist what is called: “maneuvering load”.
- If this weight information is not available, it should be calculated immediately with some certainty.
- The size of the item to be transported must be known.
- In order to execute the maneuvers of transporting suspended loads without risks, the supervisors, the crane operator, and the signalman must know the basic rules of safe suspension techniques.
- The lifting capacity of the mechanical equipment that will execute the maneuver must be known with certainty.
- Know the speed of the mechanical lifting equipment, verify if it is adequate to the programmed maneuver.
- The lifting techniques of loads must be known, according to the nature of the flanges that are being used. Especially it’s capacity and fragility.
- The intrinsic risk of the material to be raised must be known. ÿ The fragility of the material to be raised must be known.
- When starting the load lifting maneuver, the operator of the crane should check:
- Balance and stability of the load, because poorly stowed loads can be released or unbalanced unexpectedly, which can create an increase in load due to dynamic blows or unexpected pendulum effects when changing positions unexpectedly.
- Degree of fixation, you can not risk slippage of the load.
- Maximum angle generated between the flanges located on the hook suspension
Lifting equipment
Tower Crane Specifications: Maneuvers loading and unloading
This safety coefficient determines the minimum resistance that the flanges must meet when they are with a suspended load. In the most common flanges, these coefficients are called maneuver loads.
The maneuvering load on the flanges used as a joining element cannot be subjected to more load than determined in the safety coefficients of each material.
The normal thing is to use safety coefficients between 6 and 4 depending on the vertical lifting equipment.
An example of the use of a safety coefficient. If a load of 6000 Kg is lifted, the safety factor is 1 and it is a critical load that will cause the flange to break. If a load of 2000 Kg is lifted, the safety factor is 4, it is a safe load.
- When raising a load of 1000 Kg, the safety factor is 6.
- When raising a load of 1200 Kg, the safety factor is 5.
- Raising a load of 2000 Kg, the safety factor is 4.
- Raising a load of 3000 kg, the safety factor is 3.
- When raising a load of 4000 Kg, the safety factor is 2.
- When raising a load of 6000 Kg, the safety factor is 1.
As the safety coefficient approaches 1, we are approaching the breaking coefficient of the flange, due to the dynamic overload when starting or stopping a lift maneuver.
The angle of separation of the flanges: Avoid angles greater than 90º, which accelerate the wear of the flange by deformation and rupture of it.
Flange types
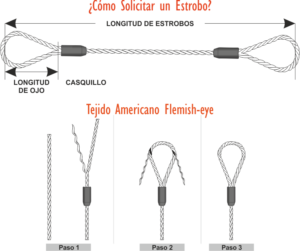
Simple bridle: It is one that is formed by a single cable, whose ends end in an eye that can be braided.
Endless bridle: It is one that has its braided ends, joining them in a single section; Your fabric or braid must be 18 times the diameter of the cable.
The flange of several branches: Are those whose branches are attached, at one end, to a ring or ring and on the other to hooks. The accessories that are used for strobing, must also have strict control regarding their capacity
Strobes for cranes
The strobes are mechanical joining elements made of steel. They are flexible and easy to manipulate. Suitable for lifting light and heavy loads. They are very resistant but deteriorate due to lack of care or storage, the main care is to prevent the formation of cokes or kinks.
In each strobe must identify the maneuvering loads, which must be written in a clear and legible, it is advisable to place a ring or a molded plate at one end. (if you do not have the information you should use the formula F = 8 d 2, d = diameter of the cable in mm, F in kg).
All strobes must be provided at each end of an eye, which must comply with current regulations. Each eye must be closed by a woven and leaded joint.
The woven and leaded finish only decreases the tensile strength of the strobe by a percentage not exceeding approximately 6%, by safety calculation this ratio must be estimated at 15%.

Steel struts
Recommendations: It is not advisable to use cable termination, its decrease, estimating that these are correctly placed, it is not less than 20%, it is normal to consider 30% with what after a stroke, the state should be carefully inspected and placement of the cable press.
The interior of the eye must be protected with a thimble, the use of this implement is intended to prevent the steel cable from over-folding.
A fold of a steel cable means a deterioration in the strength and duration of the latter, due to deformation and loss of solidity between strands.
Whatever the diameter of the steel cable, always the thimble that is used must respect proportionally the diameter of the steel cable.
Cable quality
The quality and construction of a cable used in strobes should be advised by the manufacturer of steel cables because it depends basically on the construction, the tensile strength, flexibility, limits of fatigue to bending and resistance to bad treatment that has each steel cable
When more than one cable is used to suspend a load (supplementary loads), the angle formed at the top vertex must be respected for each pair of cables, in order to resist within the safety coefficients the greater traction generated by the resultant new triangle of forces.
Transportation and storage
The strobes are transported horizontally deposited without crushing them or forcing their normal curvature and avoiding friction between them.
The strobes are only cleaned with a slightly damp cloth with a degreasing liquid (detergent), taking care to avoid the penetration of liquid by dripping into the bundles of strands.
Crane sling
Slings are flexible elements, designed to lift and handle loads, constructed with tapes woven with the polyester of tenacity to 35 mm to 304 mm wide, with thickness from 3.5 mm to 12.6 mm.
There are slings of one layer (simple), two layers (double), and three layers (triple).
Chains for cranes
The chains are flanges constructed of metal links. They have limited use due to their weight and the fact that their links wear out or deform causing their breaking without warning. Care must be taken to avoid twisting or kinking the chain while it is under load, even if it is light, since the link may break or deform.
They are suitable for lifting heavy loads such as rails, beams, angled profiles, and pipes. For the use of chain flanges, the following must be kept in mind:
- The links in the chain should be identical to be used in pairs.
- You have to determine the maximum weight of the load you plan to lift with them.
- You have to choose the appropriate chain to the load, considering the angle of work.
- Determine the point of support of the main link that will hold the hook.
- Select the components (ring, hook or both), and the way in which it is attached to the load.
- The use of chain ties should be fixed with rings or hooks on each end or the combination of both.
- Avoid using chain flanges at Tº below zero, as they become fragile
- Tighten without pulling.
- Check that all your links lie flat.
- After being used, store away from moisture and corrosive.
- Inspect the link weld.
- No chain must be subjected to a tensile force that exceeds its safety factor, set to 1/5 of its safety factor.

The resistance of a chain is as low as the strength of the most used link, therefore it is necessary to discard any chain flange, even if it is a link that decreases its diameter by 5%, it is corroded, twisted, elongated, flattened, open or simply stuck.
Stainless steel cable ties
Working with simple and composite flanges: In the use of sliding knots, it is very dangerous for the strobe to pass through the eye without having a thimble.
The most frequent work done is to lift a load with a flange vertically, where its traction (F) will depend on the angle and if it is also made with a sliding knot.
With two simple flanges, forming a 90º angle, the traction to which it is subjected is 700 Kg per flange. The weight is still 1000 Kg, but the effort made by the flanges is 700 Kg each. F = 1400 Kg.
With two simple flanges, forming an angle of 120º, the traction to which it is subjected is 1000 Kg, but the effort made by the flanges is 1000 Kg each.
With a simple flange, we can form different angles, where the traction to which it is subjected is F. The weight is still 1000 Kg, but the effort made by the flanges is different. The increase in F is due exclusively to the angle formed by the sliding knot.
How much does it cost to hire a tower crane?
The typical fee for installation and disassembly runs around $60,000. This price includes shipping the crane to the site, renting the mobile crane used to assemble the tower crane, the cost of the crew that handles the assembly, etc.
A Crane or Tower Operator will usually earn a wage of around 40000 and 60000 based on education and experience. Crane and Tower Operators usually receive an average pay level of Fifty Thousand One Hundred dollars on a yearly basis.
The most read

Tower Crane Cab
Cab features include improved seat position and access, a USB port and optional Bluetooth. A user-friendly multifunction touch screen emits warning lights and sounds, as well as controls the interior temperature, interior, and exterior lighting and other features.

Remote Control Tower Crane
Radio remote controls are now standard equipment on most self-erecting tower cranes and are even becoming common in some parts of Europe for a flat-top tower crane.
